Learn traditional Chinese medicine knowledge for health preservation and share a healthy life! Camel pose on official account is a backward bending pose that I like very much.
Although many factions feel that this is not a difficult pose, few people can do it correctly during practice.
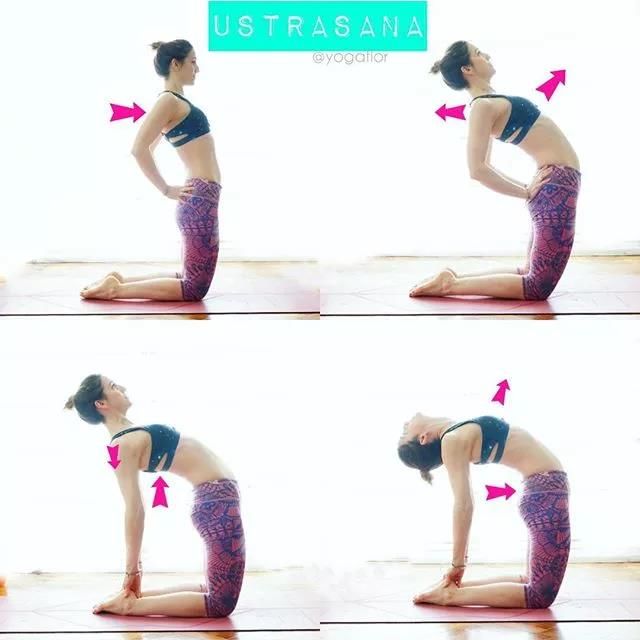

Camel style English name: Camelpose, Sanskrit name: Ustrasana, Ustra means camel.
When practicing this pose, the chest is on top and the movements are like a camel, hence the name “Camel pose”.
Let’s first take a look at the benefits of Camel pose: stimulating the spine and spinal nerves, promoting blood circulation, and thereby improving spinal function; Adjust and massage internal organs such as the waist and abdomen; It can also help eliminate thigh fat; Expand the chest to prevent sagging; Rectifying poor posture and treating hunchback; Beautify the lines of the chin; Make the spine and shoulders soft, relieve back pain and shoulder pain problems; Improve respiratory system problems; Nourishing the pelvic area, regulating menstruation, and alleviating discomfort during menstruation; Stimulate the work of the thyroid and kidneys, regulate endocrine function; Promote digestion, relieve constipation, and maintain the female reproductive system.
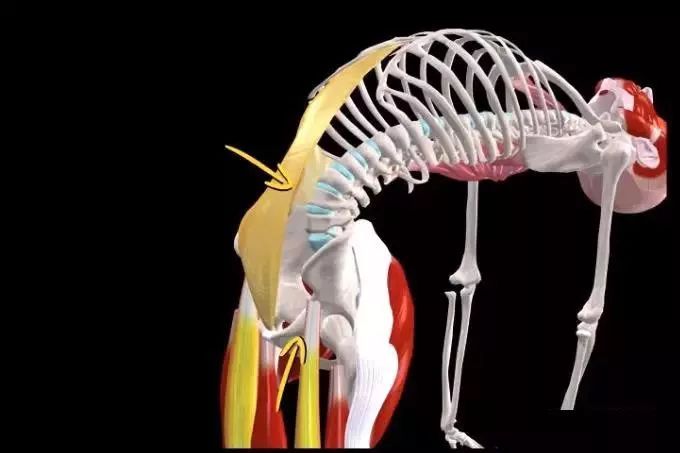
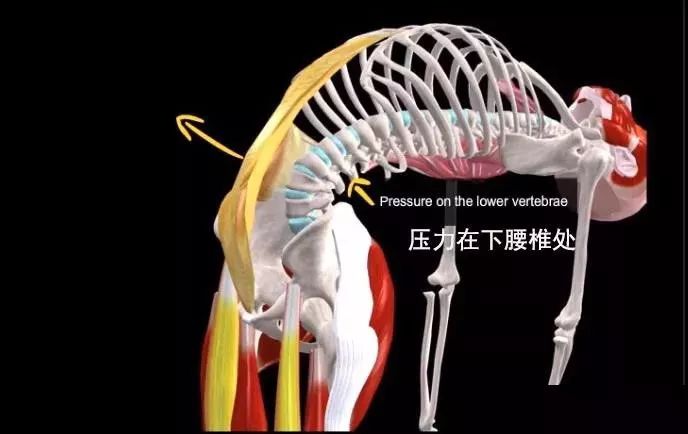
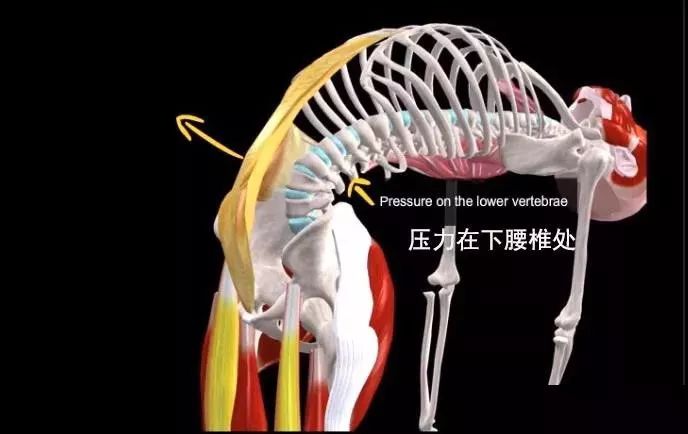
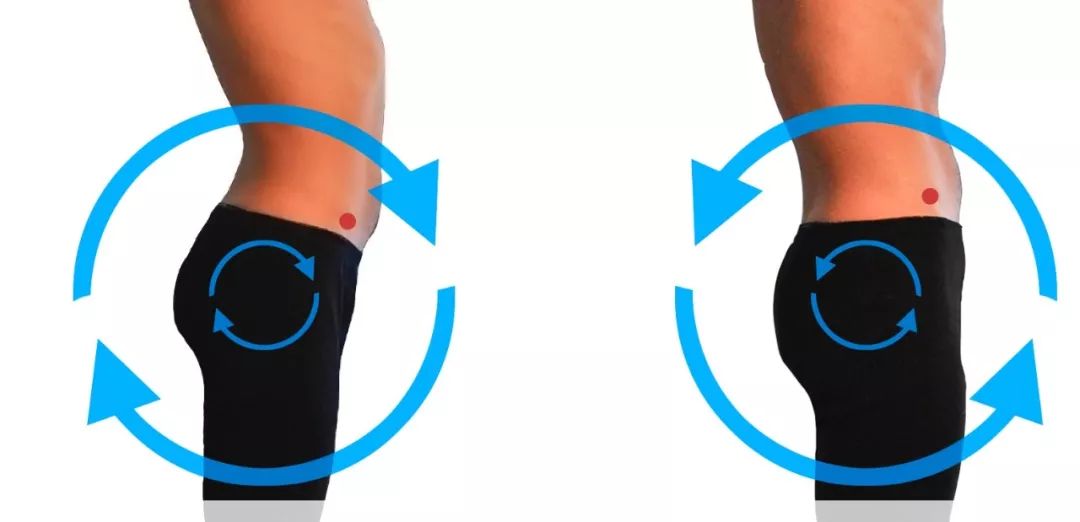
Please note that individuals with lumbar disc herniation or cervical spondylosis are prohibited from practicing! People with thyroid function problems, lumbar discomfort, or back pain can reduce the practice of this pose; It is best to avoid doing this pose if you have neck injuries, or if you have low or high blood pressure; The thighs are perpendicular to the ground, the hips are directly above the knees, the chest is pushed forward and lifted up, the head is relaxed without squeezing the cervical spine, and the back of the foot is pressed against the ground; During the practice process, always keep the pelvis aligned to reduce the stress on the lumbar spine and fully stretch the lumbar muscle group.
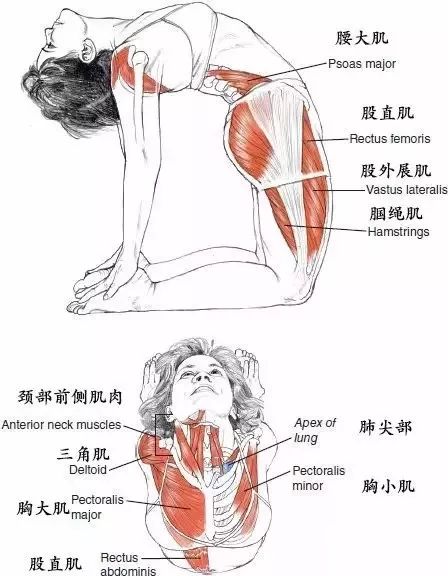
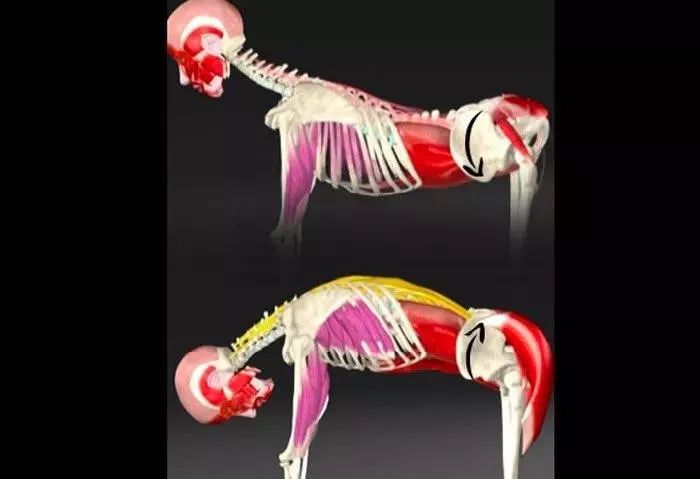
Then we dissect the camel pose together: joint movement and spinal extension; Hip joint extension and internal rotation; Knee joint flexion; The scapula rotates downward, adducts and lifts upward; Arm rotation, extension, adduction, elbow joint extension.
The working mechanism of muscles is that gravity pulls the trunk back, but it is controlled by arm movements and eccentric movements of the spinal flexor muscle group.
Arm: The triceps brachii muscle extends the shoulder and elbow joints; The trapezius and rhomboid muscles adduct the scapula.
The posterior part of the deltoid muscle muscle and the teres major also extend the shoulder joint, while the subscapularis protects the shoulder joint in front.
Spine: In the cervical segment of the spine, the muscles on the anterior side of the neck (such as the long head muscles, long neck muscles, rectus anterior head muscles, suprahyoid muscles, and infrahyoid muscles) undergo eccentric movement to prevent excessive head extension.
The muscles that can also prevent excessive extension of the lumbar segment of the spine through eccentric exercise include rectus abdominis, oblique abdominis (especially external oblique abdominis), intercostal muscle, subcostal muscles, iliac muscles, psoas major muscle muscles and psoas minor muscles
.